Area Scanners
When there is a moving robot, equipment or machinery in a system, it is important to identify, define, and protect against all hazards. In the past, this was predominantly done with physical barriers, such as fencing and gates, that restrict access to an area with the potential hazard. These barriers may solve the safety issue but bring new issues that cost manufacturers downtime and efficiency.
Fences must contain the entire robot system. The fenced-in area has an entry gate process that requires an access request from the operator, the robot stops at a good stopping point, the operator enters the fenced area, works, leaves, resets the system, and the robot starts moving again.
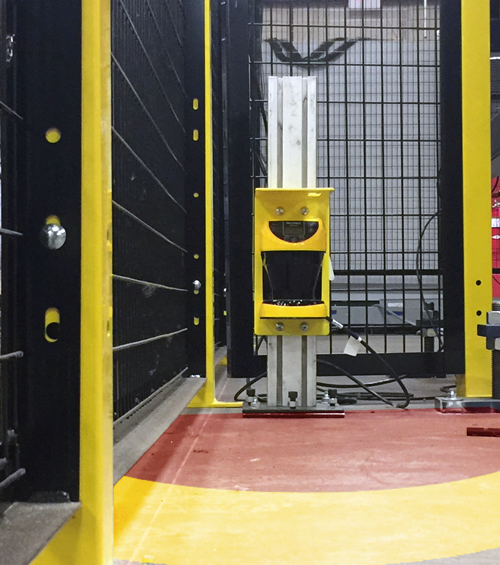

Likewise, area scanners allow for protection zones to be defined, but without fencing. The operator requests access to the area, enters, finishes work, and then resets once they leave the area. One can work safely, and the scanner slows or stops the operation at a known stopping point only when someone or something is in a defined zone. Robot and system movement only resume once the someone or something has left the area.
If the operator does not request access and enters the area the system will fault and come to a stop. This takes more time because the robot isn’t able to stop at the known stopping point, and has to cycle back to the correct position.
Area Scanner Setup
Area scanners keep both people and equipment safe. Protection and warning zones can be configured with flexibility and adapted to structural conditions.
Area scanners use time-of-flight technology to calculate the protection zones. The scanner calculates the time it takes for a laser to bounce off an object and return to the sensor.
Zones
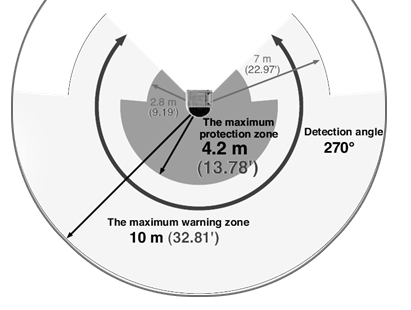
Scanners can be mounted vertically or horizontally and the graphic to the right shows a general coverage of an area scanner. An area scanner monitors a 2D area of a 190-degree angle with several meter radius.
Warning Zones
- Can be configured and drawn around permanent or predicted obstacles.
- The warning zone in this example is anytime the person or object is within 32.81 feet (10m) of the hazard.
- If the scanner detects an object in the specified warning zone, a light can flash, warning message be displayed, or audible tone can be heard.
Protection Zones
- Can be configured and drawn around permanent or predicted obstacles.
- The protection zone begins when the person or object moves to within 13.78 feet (4.2m).
- If the scanner detects an object in the specified protection zone, the OSSD (output signal-switching device) changes to the OFF-state to stop the machine hazard.
- The moving hazard stops completely so the person or object can safely work in the area and then restarts when the protection area is clear. Some operations will automatically restart, but others may require the operator to initiate a restart of the system.
Certain Area scanners can be set up for multiple protection and warning zones. These can be used when there are multiple moving hazards and it is safe to enter one area but not another.
Area Scanners vs Light Curtains
Another common safety feature in robot systems is light curtains. Light curtains work by sending optical beams from an emitter across a work area to a receiver unit. When the beam is broken, hazardous motion comes to a stop. This means light curtains are the best option for very fast response time. These beams can sense even small intrusions into the space – such as fingers. Another positive feature about light curtains is they can be programmed to distinguish between humans and product. This operation is called light curtain muting.
Light Curtain Example
One example of light curtain muting is where there is an opening in guarding that’s protected by a light curtain, but product (i.e. pallets with product) must travel on a conveyor through the light curtain. A Muting Controller or Safety PLC can accomplish this muting function by using sensors and the light curtain to safely suspend the light curtains safety function for product to move through the light curtain without stopping the system. The controller or Safety PLC does this by evaluating the signals from the sensor and light curtain to ensure they are turning on and off in a specific sequence within a specific time frame. Once the product moves past the sensors and light curtain the light curtain safety function immediately starts functioning again.
Wrap-up- Light Curtains
Light Curtains respond quickly to even small objects and simplify routine tasks, pallet movement, and maintenance.

Area Scanner Example
The operator needs to replenish parts and can do so safely at a defined distance from the robot. If for some reason, the operator enters the warning zone, the robot slows. If the operator enters the protection zone, the robot will come to a complete stop.
An equipment protection example would be if there are several moving items in a cell, such as a robot and a rail that transfers parts.
Wrap-up- Area Scanners
- Area scanners are not only used to protect operators but are also for machine safeguarding.
- Customize protected area to match the floor space.
- Detect the approach of objects in larger areas.
- Area scanners are not used for areas needing a fast reaction time.
Select the best option
- A robot system has palletized product leave the cell on a moving conveyor.
- Light curtain with light curtain muting, fencing, and a gated entry- Product can move through the open area and any other intrusions stop the movement. Operators enter only through the gate.
- A robot system transfers pallet to an area (still inside the robot cell) where a fork truck picks the pallet
- Fence with gate entry and an area monitored with an area scanner for the fork truck to pick pallets. Allows the operator to request access to the cell using a pull cord without having to get down from the fork truck.
Area scanners can be used in
Robot Cells
Area scanners can be used to monitor the hazardous area directly around the robot and either slow or stop the robot when the operator enters the cell or is in a hazardous area. This is very helpful in keeping production running at a consistent and efficient pace. 
AGVs Mobile Mounting
A safety laser scanner can be mounted on Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs) like a transfer cart to eliminate the risk of collisions with objects or people in its path and help to eliminate unnecessary stoppage.
The area scanner mounted on an AGV can use multiple warning and protection zones for effective and safe operation. Examples of these zones can be a slowdown zone and safe stopping zone.
Other moving machinery in a system
Any moving equipment that could be a hazard to workers and would benefit from the programming of zones to reduce speed or completely stop a process.
Second line of safety
Area scanners added to robot cells in conjunction with a safety gate to ensure no one is in the cell if the safety gate is closed. While there is someone or something in the protected zone, the hazardous movement will not restart.
The example area scanner shown in this Tech Talk article is manufactured by Keyence. Contact them if you would like to add an area scanner to your current system.
If looking to integrate a robot into your process, know that there are options available to make the process more flexible.